Introduction
Feeding accuracy is one of the most important performance indicators for screw feeders.
For overseas users (US, Europe, Asia), the question “How stable is the feeding accuracy?” is always a major topic.
Accuracy is not determined by screw speed alone — powder characteristics, feeder design, surrounding environment, and operating conditions all interact.
This article explains the five key factors that significantly influence feeding accuracy.
1. Powder Characteristics (Flowability, Bulk Density, Hygroscopicity)
The most critical factor affecting feeding accuracy is the nature of the powder itself.Powders with poor flowability (hygroscopic materials, fine powders, cohesive powders) tend to cause fluctuations,while free-flowing powders (granular or dry materials) typically produce stable feeding.
Key points:
- Hygroscopic powders: feeding rate may drift over time
- Low-density powders: voids form inside the screw, creating instability
- Cohesive powders: lumps may discharge intermittently
Knowing particle size, bulk density, and angle of repose helps estimate expected accuracy.
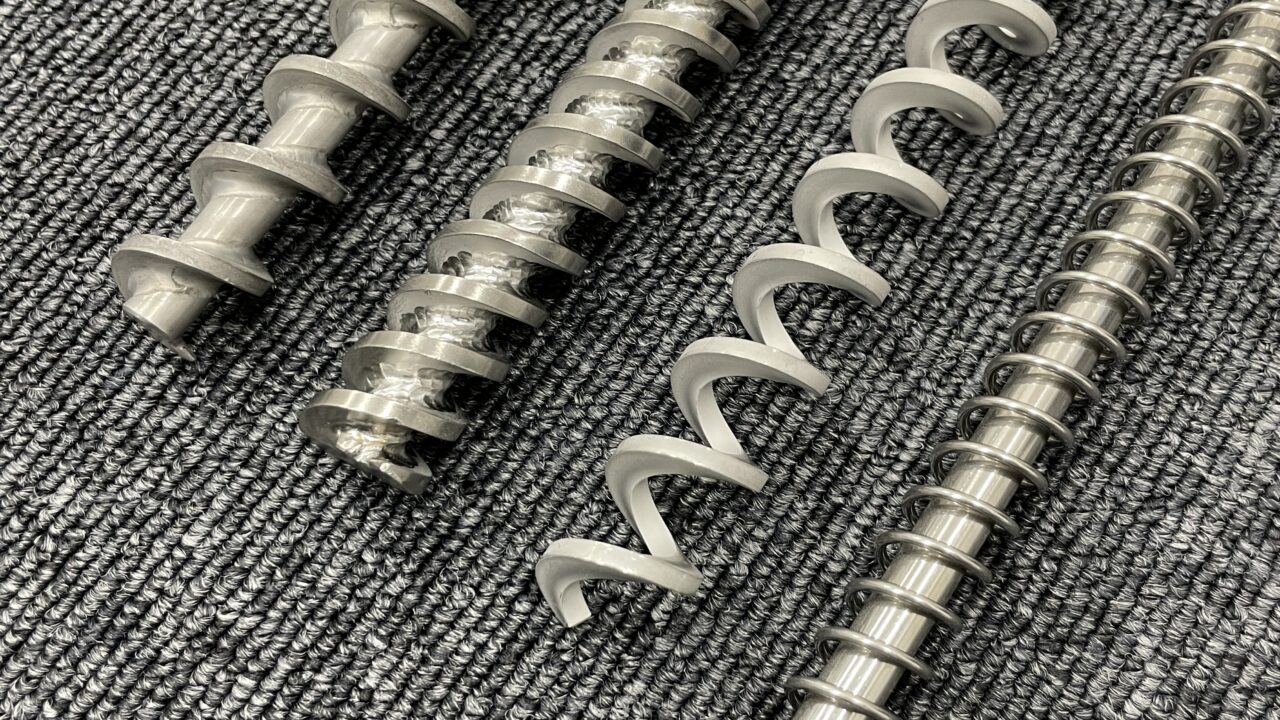
2. Screw Geometry (Pitch, Diameter, Shaft Type)
The screw’s design has a direct impact on feeding accuracy.
Key design elements:
- Screw diameter: smaller diameters suit micro-feeding but may clog more easily
- Pitch: shorter pitch stabilizes feeding; longer pitch increases capacity
- Center shaft: with shaft → stable accuracy; shaftless → suited for high-capacity feeding
Selecting the right screw design for the powder reduces fluctuations in continuous feeding.
3. Hopper Design (Discharge Behavior, Anti-Bridging Features)
Many feeding accuracy problems originate from hopper design issues, not the screw itself.
Accuracy-related hopper conditions:
- Shallow angles cause bridging or ratholing
- Small hoppers may not provide stable powder supply to the screw
- Dead zones create inconsistent feeding due to material buildup
If powder cannot fall consistently into the screw, increasing RPM will not improve accuracy.
4. Environmental Conditions (Humidity, Vibration)
Screw feeders are sensitive to external environmental conditions.
Common influences:
- High humidity: powders absorb moisture, reducing flowability
- Equipment vibration: can cause overfeeding or clogging
- Temperature changes: may promote cohesion or moisture absorption
Hygroscopic powders such as sugars, battery materials, and metal salts are especially sensitive.
5. Operating Conditions (RPM Setting, Startup Behavior)
Feeding accuracy is also affected by how the feeder is operated.
Operational factors that affect accuracy:
- Higher RPM tends to reduce feeding fluctuation
- Accuracy is often lower immediately after startup
- Long-term running may alter powder characteristics and reduce stability
Understanding these behaviors and adjusting operation parameters improves consistency.
Conclusion
Feeding accuracy in screw feeders is determined by a combination of:
powder characteristics × screw design × hopper structure × environment × operating conditions.
For overseas users, environmental differences and equipment layout variations make it particularly important to share powder information and optimize feeder specifications.
Seiwa Giken Mini / Standard Screw Feeder Introduction
Seiwa Giken provides Mini Screw Feeder / Standard Screw Feeder designed for high accuracy and stable feeding, with screw and hopper configurations optimized for various powder characteristics, making them highly reliable for international users.
👉 Learn more about Seiwa Giken’s Screw Feeders↓↓