Understanding and Preventing Powder Bridging in Screw Feeder Powder Feeding Systems
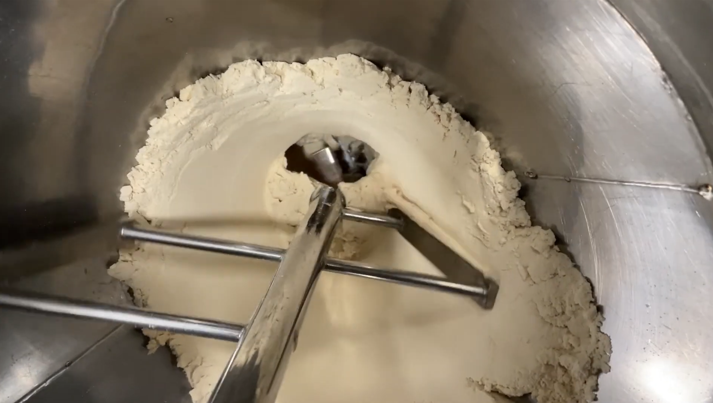
Powder bridging is a common problem in powder feeding processes, especially when using screw feeders. It occurs when powder particles clump together and form a bridge or arch inside the hopper or feeder, blocking the continuous flow of material. This blockage can disrupt the feeding rate, reduce accuracy, and negatively impact production efficiency.
What is Powder Bridging?
Powder bridging happens when fine powders or granulated materials with certain physical properties (such as cohesiveness, moisture content, or particle size distribution) stick together and form a stable arch inside the feeding system. This arch prevents powder from flowing freely into the screw feeder, leading to interruptions or stoppages in the feeding process.
In screw feeder powder feeding, consistent and accurate powder flow is essential for dosing, mixing, and processing operations. Powder bridging directly compromises these goals by causing irregular feeding rates or complete stoppage.
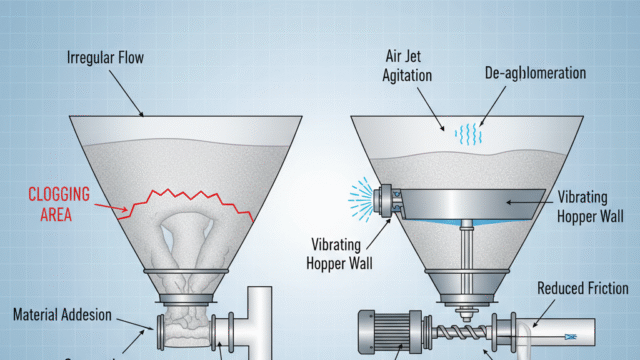
Causes of Powder Bridging in Screw Feeders
Several factors contribute to powder bridging during screw feeder powder feeding:
- Powder Characteristics: Highly cohesive powders, powders with high moisture content, or powders with irregular shapes tend to bridge more easily.
- Hopper Design: Inadequate hopper angles or improper outlet sizes can encourage bridging formation.
- Feeding Speed: Low screw rotation speeds may fail to break powder arches effectively.
- Environmental Conditions: Humidity and temperature affect powder flowability.
How to Prevent Powder Bridging in Powder Feeding Systems
To improve powder flow and prevent bridging in screw feeder feeding systems, consider the following solutions:
- Optimize Hopper Design: Ensure hopper angles are steep enough (typically above 60 degrees) to encourage gravity flow and avoid stagnant powder zones.
- Use Agitation or Vibration: Installing a shaker or vibrator can break powder bridges and improve flow consistency.
- Adjust Screw Feeder Settings: Increasing screw rotation speed or using specialized screw designs can reduce powder compaction and bridging risk.
- Control Environmental Conditions: Maintaining low humidity and stable temperature helps keep powder dry and free-flowing.
- Material Conditioning: Adding flow agents or drying powders before feeding can improve powder behavior.
Why Choose a Screw Feeder for Powder Feeding?
Screw feeders are widely used for powder feeding because they offer precise control over powder feed rates, can handle a variety of powder types, and allow customization to specific applications. However, to maximize performance, preventing powder bridging is crucial.
By understanding the causes and implementing proper system design and operational strategies, powder bridging can be minimized, resulting in stable, accurate powder feeding with screw feeders.
PLEASE VISIT OUR WEBSITE