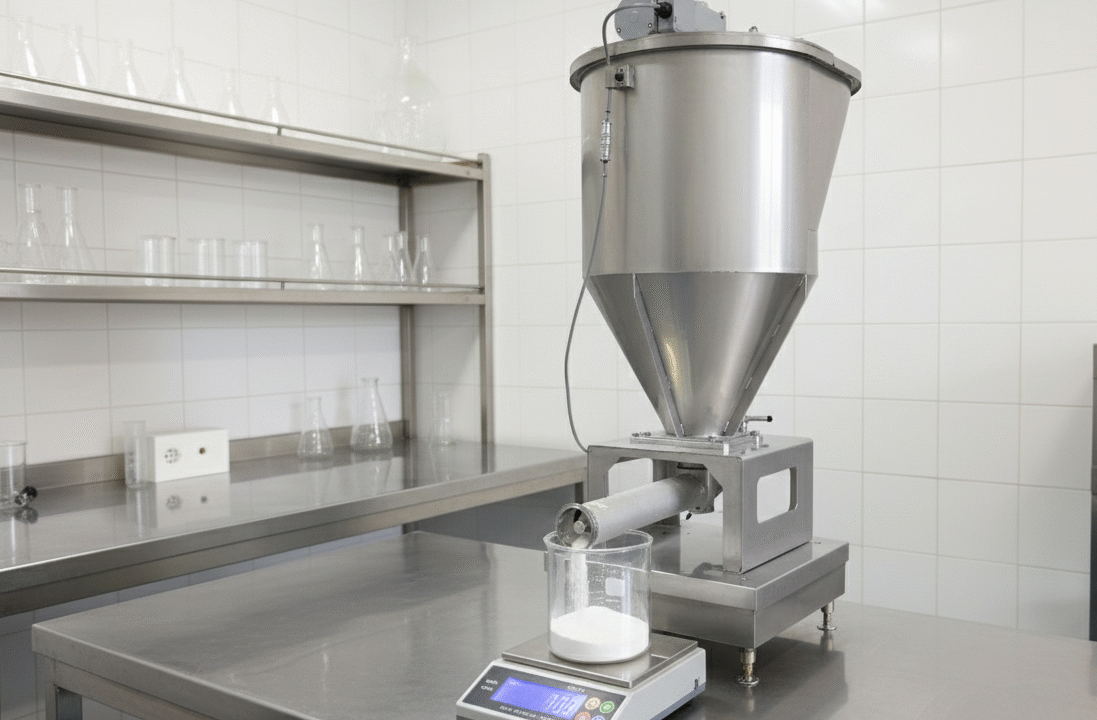
1. What Is Screw Feeder Accuracy?
Accuracy in a screw feeder refers to how consistently the feeder can deliver the target feed rate.
The actual performance varies depending on powder characteristics, feeding method, and the mechanical design of the equipment.
In overseas markets—especially where yield improvement, automation, and labor savings are priorities—high feeding accuracy is increasingly important.
2. Key Factors That Affect Accuracy
Screw feeder accuracy cannot be determined by screw speed control alone. Multiple factors interact to influence stability.
2-1. Powder Characteristics (Flowability, Adhesiveness, Bulk Density)
- Low-flowability powders tend to pulse or bridge.
- High adhesiveness causes inconsistent discharge.
- Low bulk density powders trap air easily, leading to unstable feeding.
2-2. Screw Geometry
- Flight pitch
- Outer diameter and shaft diameter
- Single screw or twin screw
Each geometry is suitable for different powders, so proper screw selection is critical.
2-3. Hopper Design and Discharge Behavior
If the hopper does not discharge uniformly, the amount of powder reaching the screw fluctuates, reducing feeding accuracy.
2-4. Control Method (Feedback vs. Open Loop)
- Load-cell-based gravimetric control provides high accuracy.
- Speed control alone cannot compensate for changes in powder behavior.
3. How to Improve Feeding Accuracy
The following countermeasures are especially valued by overseas users.
3-1. Select the Right Screw Type for Each Powder
Examples:
- Highly adhesive powders → Twin screw
- Lightweight powders → Coarse pitch + anti-pulsation design
- Viscous powders → Coreless (hollow) screw
3-2. Add Hopper Anti-Bridging Measures
- Aerator
- Vibrator
- Agitator inside the hopper
These devices stabilize powder supply, improving accuracy.
3-3. Use Load Cells for Feedback Control
In Europe and the U.S., gravimetric feeders are often preferred.
Real-time weight feedback significantly improves accuracy.
4. Accuracy Requirements in Overseas Markets
Recent trends in Europe, the U.S., and Asia:
- ±1–3% accuracy is commonly required for continuous feeding.
- Laboratory applications may require ±0.5% or higher accuracy.
- Food, pharmaceutical, and battery materials often demand stricter control.
High-accuracy applications require customized designs based on powder properties.
5. Summary
Screw feeder accuracy is determined by the combination of:
Powder characteristics × Screw geometry × Hopper design × Control method
It is important for overseas users to understand that accuracy cannot be controlled by screw speed alone.Improving accuracy requires optimizing all related factors together.
Seiwa Giken’s screw feeders, including Mini and Standard types, are designed with these factors in mind, offering stable, high-precision powder feeding for a wide range of applications.
👉 Learn more about Seiwa Giken’s Screw Feeders↓↓